Date First Published: 4th February 2022
Topic: Computer Networking
Subtopic: Data Transmission Technologies
Difficulty: EasyDifficulty Level: 3/10
Learn more about what Bluetooth is in this article.
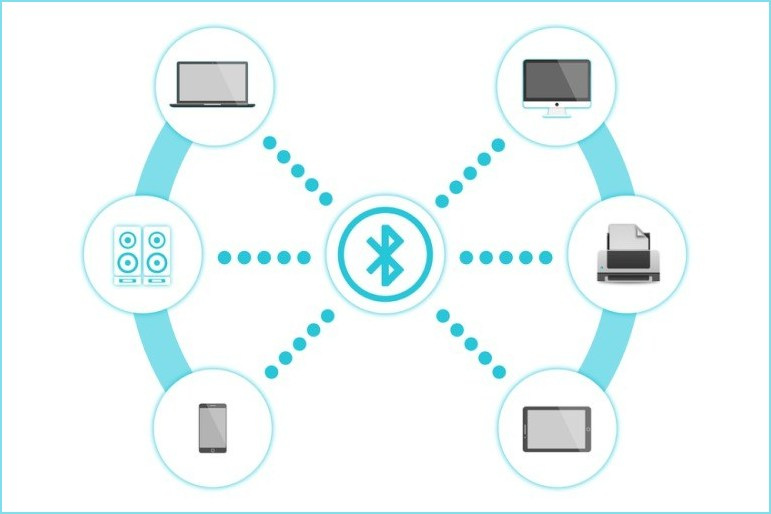
Bluetooth is a high-speed wireless communication technology that uses low-power radio waves in order to allow two electronic devices to connect and transmit information over short distances without the need for any wires. The most common uses of Bluetooth are to share files between devices and connect other wireless devices to a computer, such as headphones, keyboards, mouses, etc. The process of connecting two Bluetooth devices is known as 'pairing'. When connecting devices together with Bluetooth, the Bluetooth device that the user wants to connect to is selected when its name or ID appears on their device.
Bluetooth was standardised by the IEEE as IEEE 802.15.1 and it is managed by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group, a non-profit and non-stock organisation that was founded in September 1998 and oversees the development of the Bluetooth standards and technologies. However, IEEE no longer maintains this standard.
Bluetooth does not require an internet connection for devices to connect. Bluetooth will work anywhere with two devices that have Bluetooth capabilities.
Bluetooth has a slower data transfer rate than Wi-Fi. This is because it is designed to use less power and be less expensive to set up than Wi-Fi. Bluetooth operates on the same 2.4GHz frequency as cordless phones and Wi-Fi routers in homes or offices. It generates a wireless network with a 10-metre diameter, known as a personal area network (PAN), which is a network of devices that are connected using Bluetooth technology. An example of using Bluetooth is sending a page to a printer that is in another room without a cable. Because of this fact, it is less likely to interfere with other wireless devices.
Bluetooth is a reasonably secure wireless communication technology as it uses an encrypted connection, reducing the chances of sensitive information being intercepted by unintended recipients. Bluetooth is more secure than Wi-Fi. In addition, a Bluetooth device cannot connect unless it is trusted by the user, which can be altered in the settings of the device.
There are some Bluetooth security risks and attacks that exist. Some examples of this are bluesnarfing and bluebugging. Bluesnarfing is a type of attack when a malicious hacker gains unauthorised access to personal information on a device through a Bluetooth connection, such as text messages, calendars, and contacts without the user knowing. Bluebugging is a step beyond bluesnarfing. It is an attack that establishes a backdoor on a user’s mobile phone or personal computer, allowing a malicious hacker to take over and gain unauthorised access to a device through Bluetooth. However, a device must have Bluetooth connection turned on and set to discoverable in order for it to be vulnerable to bluesnarfing or bluebugging.
Never connect to unknown Bluetooth devices. It might be a device that performs malicious actions, such as collecting sensitive information or gaining remote access to your device.

The Bluetooth resembles two and a half triangles pointing to the right. It is a combination of the two initials that were used in the Viking Age by Harald Bluetooth, "H" and "B". These initials were merged, creating a bindrune.
The word 'Bluetooth' comes from a Danish king called Harald Bluetooth, who was around in the 10th century and known for uniting Denmark and Norway together in the year, 958. The word 'Bluetooth' came from his dead tooth, which was a dark blue colour and gave him the nickname, Bluetooth. The technology was developed in 1994 to replace cables with more modern wireless technologies, although it was not officially introduced until 7th May 1998. The first phone that was capable of connecting to Bluetooth was not until 2001.
Intel, Ericsson, and Nokia, three business leaders, met in 1996 to discuss the standardisation of this short-range radio technology to allow communication and collaboration between various products and industries. During the discussion, Jim Kardach from Intel suggested the term Bluetooth as a temporary code name. Kardach was later quoted as saying, "King Harald Bluetooth was famous for uniting Scandinavia, just as we intended to unite the PC and cellular industries with a short-range wireless link."
If so, it is important that you tell me as soon as possible on this page.
Network Services Network Setups Network Standards Network Hardware Network Identifiers Network Software Internet Protocols Internet Organisations Data Transmission Technologies Web Development Web Design Web Advertising Web Applications Web Organisations Web Technologies Web Services SEO Threats To Systems, Data & Information Security Mechanisms & Technologies Computer Hardware Computer Software Ethics & Sustainability Legislation & User Data Protection