Date First Published: 8th April 2024
Topic: Computer Systems
Subtopic: Computer Software
Article Type: Computer Terms & Definitions
Difficulty: MediumDifficulty Level: 5/10
Learn about what a process is in this article.
A process is an instance of a program being run on a computer. Each time a program is actively run by the CPU, a process is started. The instructions from the source code of the program and any resources required for it at that time (such as input, output, and intermediate data) are included in each process, which can have one or more threads.
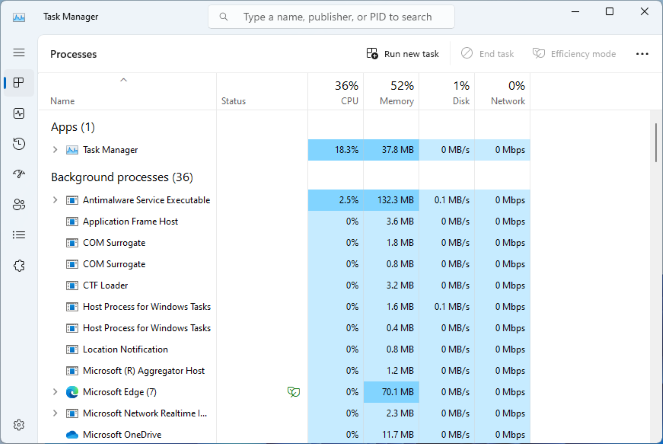
Operating systems provide utilities that allow users to see what processes are running on their computers. For example, Windows Task Manager provides detailed insights into the performance of the computer and resource usage and allows users to manually terminate processes, adjust processing priorities, and view information about users currently logged onto a system.
To help prevent conflicts and ensure data security, independent processes from different programs are generally not allowed to directly communicate with each other. But, a process has the ability to start a subprocess, sometimes known as a child process (the process that started it is sometimes referred to as its parent).
Although a child process is a copy of its parent process and uses some of its resources, it can no longer exist if the parent process is terminated. For example, a web browser may start a separate process for each tab, browser extension, or plugin and those separate processes will terminate if the main web browser process is terminated. Processes can also exchange information or synchronise operations through different methods of interprocess communication (IPC).
Modern operating systems support multitasking, which allows multiple applications or processes to run at once. Multitasking makes it possible for multiple programs, like word processors, web browsers, and file explorers, to run at the same time.
The operating system's task scheduler organises CPU time between processes based on priority, quickly switching between them to keep them running almost at the same time. Since interactive processes often have the greatest priority, resources are allocated to them quickly in response to user input such as keystrokes and mouse clicks, whereas background processes must wait their turn.
If so, it is important that you tell me as soon as possible on this page.
Network Services Network Setups Network Standards Network Hardware Network Identifiers Network Software Internet Protocols Internet Organisations Data Transmission Technologies Web Development Web Design Web Advertising Web Applications Web Organisations Web Technologies Web Services SEO Threats To Systems, Data & Information Security Mechanisms & Technologies Computer Hardware Computer Software Ethics & Sustainability Legislation & User Data Protection