Date First Published: 23rd January 2022
Topic: Computer Networking
Subtopic: Internet Protocols
Article Type: Computer Terms & Definitions
Difficulty: AdvancedDifficulty Level: 9/10
Learn about what DNS cache is in this article and how to view and flush it.
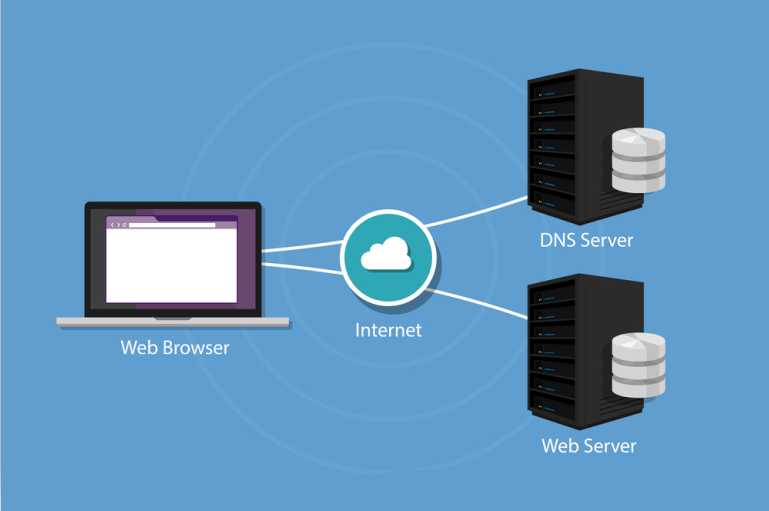
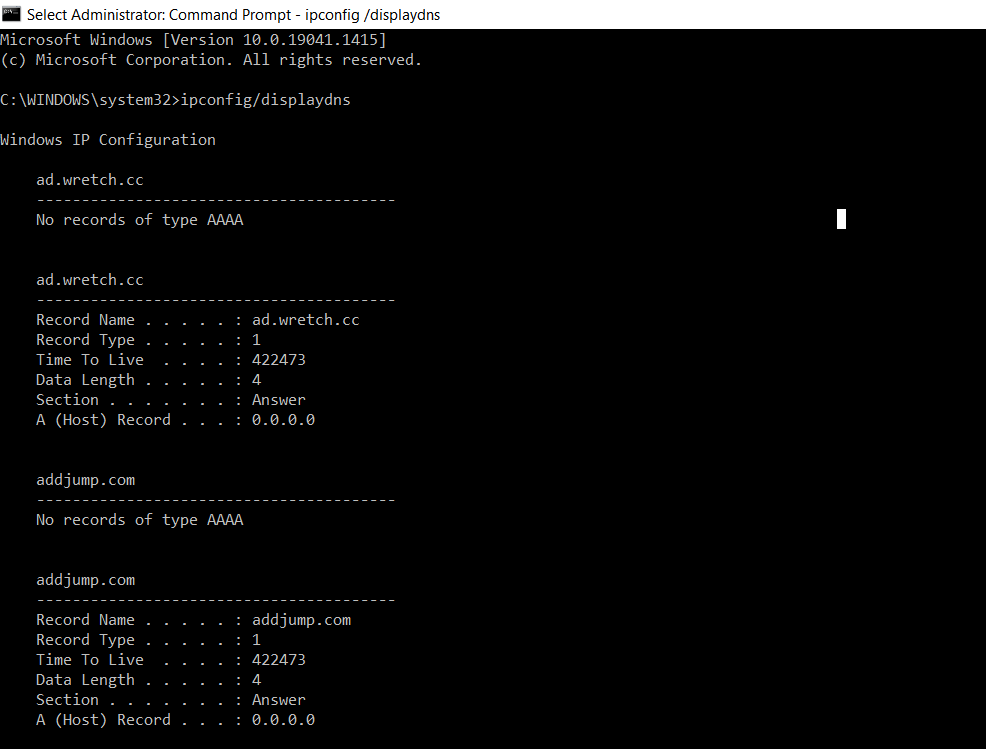
DNS cache temporarily stores previous DNS lookups on a computer in order to retrieve the IP addresses and translate domain names into IP address quicker, reduce the number of full DNS lookups that are requested from browsers, and overall speed up the DNS process. It is similar to browser cache as it temporarily stores a copy of all pictures, CSS, and JS files in order to make webpages load quicker. When viewing DNS cache, it basically contains a record of all recently visited websites, since every domain name requires a DNS lookup to be fully performed before it is saved in DNS cache. In addition, DNS cache can be useful for remembering a website that was previously visited as it stores a list of all previously visited websites, even if the browsing history is cleared.
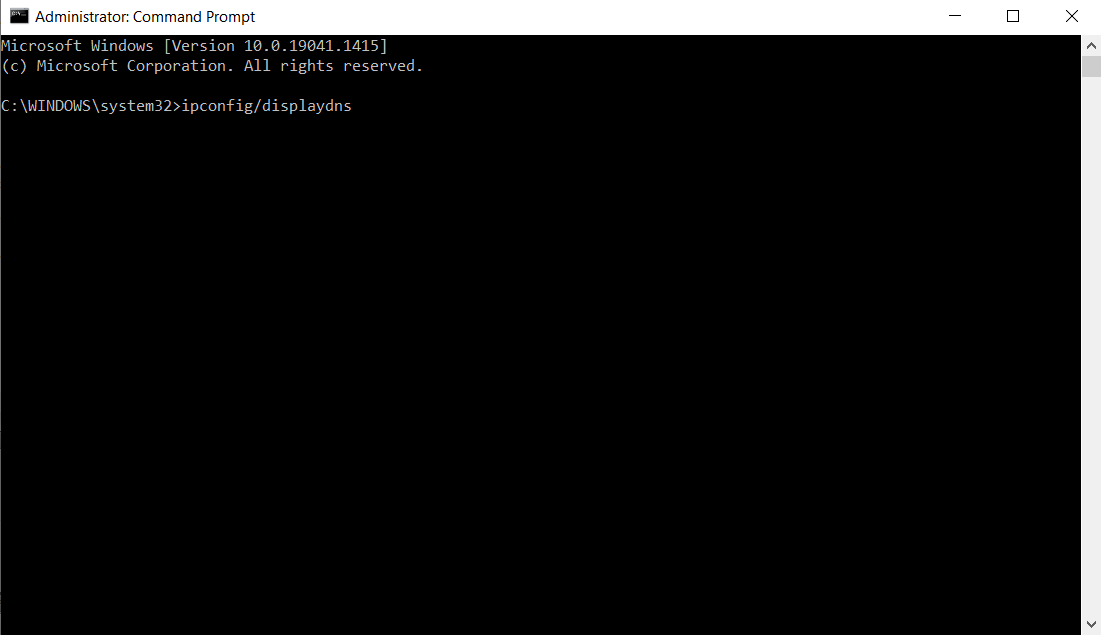
Viewing the DNS cache on Windows will display the temporary database of all recent DNS lookups and visits to websites. These steps below can be used for viewing the DNS cache on Windows.
Flushing DNS cache means to clear and remove all of the temporary storage of previous DNS lookups from a computer. This is useful for resolving DNS-related errors that prevent websites from loading, but previously visited websites may load slower after flushing DNS cache since full DNS lookups will be required. The first two steps that need to be carried out are exactly the same as the previous guide, which was about viewing DNS cache. The difference in these steps is that the command that needs to be typed into Command Prompt in order to flush DNS cache is 'ipconfig/flushdns', instead of 'ipconfig/displaydns'.
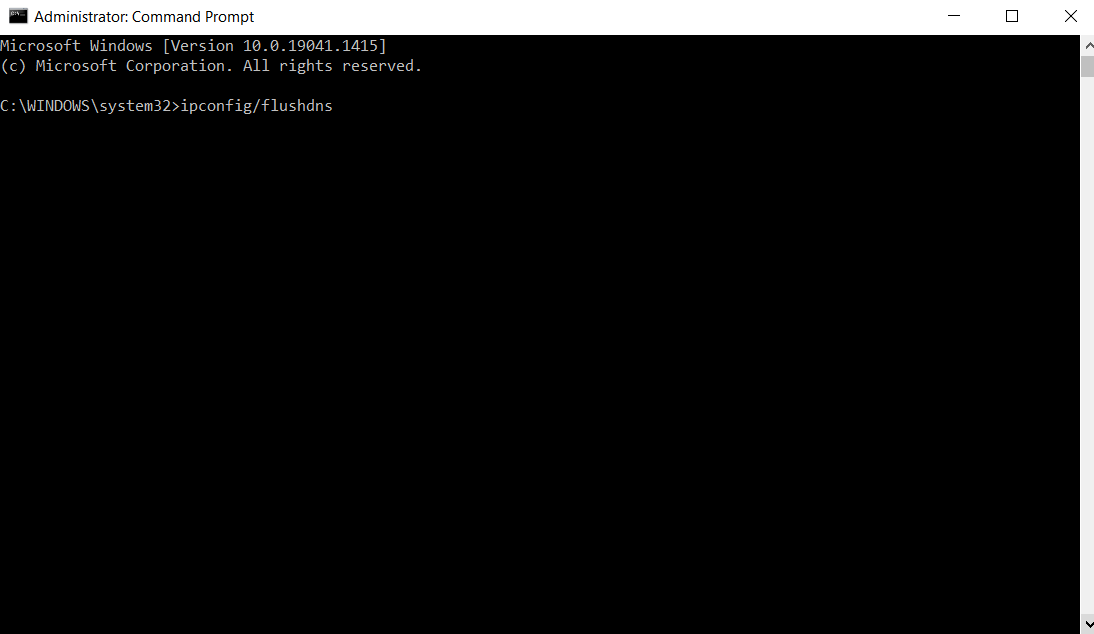
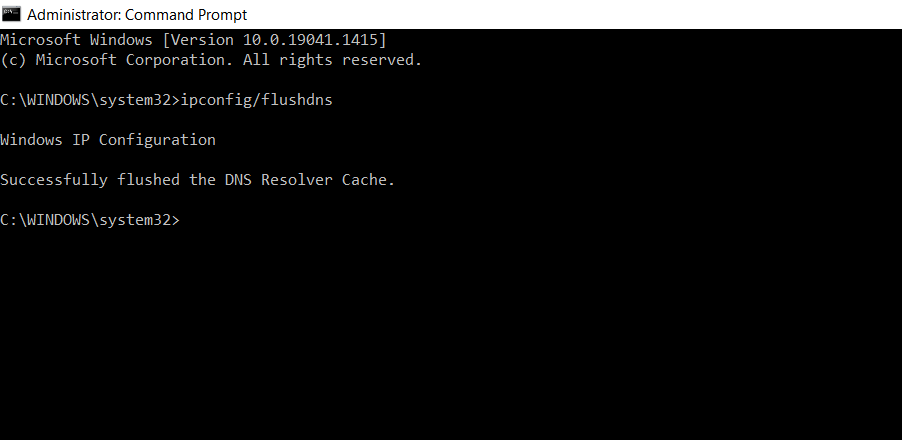
Tap 'Enter' and the DNS cache should be flushed. When the DNS cache is successfully flushed, a message should appear, saying 'Successfully flushed the DNS resolver cache' as seen in the screenshot below.
Close any web browsers and open them again. In order for the flushed DNS cache to successfully take effect, it is necessary to close any web browsers and then reopen them.
If so, it is important that you tell me as soon as possible on this page.
Network Services Network Setups Network Standards Network Hardware Network Identifiers Network Software Internet Protocols Internet Organisations Data Transmission Technologies Web Development Web Design Web Advertising Web Applications Web Organisations Web Technologies Web Services SEO Threats To Systems, Data & Information Security Mechanisms & Technologies Computer Hardware Computer Software Ethics & Sustainability Legislation & User Data Protection